Comprehensive Guide to Muscle Pain Knee Treatment: Remedies, Exercises, and Prevention Strategies
Introduction:
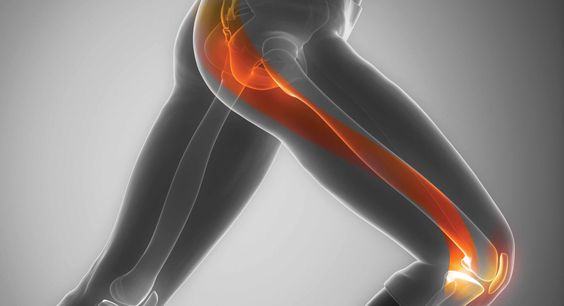
Muscle pain in the knee is a common issue that can be caused by various factors such as overuse, injury, poor posture, or underlying medical conditions. Regardless of the cause, managing muscle pain in the knee is essential for maintaining mobility and preventing further complications. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights into effective treatment options, including remedies, exercises, and prevention strategies to alleviate muscle pain in the knee.
Pain o soma 500mg It seems to be an attractive option for relieving nerve-related discomfort. Nevertheless, there are significant concerns over the medication’s efficacy and safety. muscular relaxants, such as Pain O Soma and others, have long been prescribed to patients suffering from aches and pains caused by things like muscular strains and spasms.
Understanding Muscle Pain in the Knee:
Before delving into treatment methods, it’s crucial to understand the anatomy of the knee and the common causes of muscle pain in this area. The knee joint is comprised of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and muscles, all of which work together to support movement and stability. When any of these structures are strained, injured, or inflamed, it can result in muscle pain around the knee.
Common causes of muscle pain in the knee include:
- Overuse injuries: Activities that involve repetitive movements such as running, cycling, or jumping can strain the muscles around the knee, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Acute injuries: Traumatic events such as falls, twists, or direct impacts can cause muscle strains, sprains, or tears in the knee.
- Poor biomechanics: Incorrect movement patterns or poor posture during physical activities can place excessive stress on the muscles around the knee, leading to pain and dysfunction.
- Medical conditions: Certain conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, tendonitis, or bursitis can cause inflammation and pain in the knee muscles.
Treatment Options for Muscle Pain in the Knee:
- Rest and Immobilization:
- Resting the affected knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
- Immobilization with the use of a brace or splint may be recommended to stabilize the knee and prevent further injury.
- Ice Therapy:
- Applying ice packs to the affected knee for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ice therapy can also numb the area, providing temporary relief from discomfort.
- Heat Therapy:
- Heat packs or warm compresses applied to the knee can help relax tight muscles and improve blood circulation, promoting healing.
- Heat therapy is particularly beneficial for chronic muscle pain or stiffness.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
- Over-the-counter NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with muscle pain in the knee.
- It’s essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional, especially if there are underlying health conditions or concerns about medication interactions.
- Physical Therapy:
- A tailored physical therapy program can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and correct biomechanical issues.
- Therapeutic exercises, stretches, manual therapy techniques, and modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation may be incorporated into the treatment plan.
- Corticosteroid Injections:
- In cases of severe pain and inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the knee joint to reduce swelling and discomfort.
- These injections provide temporary relief and are typically used in conjunction with other treatment modalities.
- Regenerative Therapies:
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or stem cell injections may be recommended to promote tissue repair and regeneration in cases of chronic muscle pain or injury.
- These regenerative treatments harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms to accelerate recovery and improve outcomes.
- Surgery:
- In rare cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues or correct underlying structural abnormalities.
- Surgical options for muscle pain in the knee may include arthroscopic procedures, ligament reconstruction, or total knee replacement, depending on the severity and nature of the condition.
Exercises for Muscle Pain Knee Treatment:
Incorporating specific exercises into your daily routine can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance joint stability. However, it’s essential to perform these exercises under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional to ensure proper form and minimize the risk of further injury. Here are some effective exercises for muscle pain knee treatment:
Prosoma 350 mg is an anti-inflammatory medication that reduces swelling and relaxes muscles after injuries or aches and pains in the muscles and joints. By affecting the transmission of impulses in the central nervous system, the active ingredient, carisoprodol, aids in muscular relaxation.
- Quadriceps Strengthening:
- Straight Leg Raises: Lie on your back with one leg bent and the other straight. Lift the straight leg towards the ceiling, keeping it straight, then lower it back down. Repeat 10-15 times on each leg.
- Terminal Knee Extension: Stand with your back against a wall and a rolled-up towel under the affected knee. Straighten the knee, pushing the back of it into the towel, then relax. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Hamstring Strengthening:
- Hamstring Curls: Stand behind a chair and hold onto it for support. Bend one knee and bring your heel towards your buttocks, then slowly lower it back down. Repeat 10-15 times on each leg.
- Bridge Exercise: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Lift your hips towards the ceiling, keeping your shoulders, hips, and knees in a straight line. Hold for a few seconds, then lower back down. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Calf Strengthening:
- Calf Raises: Stand with your feet hip-width apart and hold onto a sturdy surface for balance. Rise up onto your toes, then lower back down. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Towel Stretch: Sit on the floor with your legs straight out in front of you. Loop a towel around the ball of your foot and gently pull it towards you, feeling a stretch in your calf. Hold for 30 seconds, then switch legs.
- Tapaday 200 mg Tablet is an opioid medication for the treatment of acute pain in adults ranging from mild to severe. You can take it to alleviate a wide range of symptoms, including headaches, fever, period discomfort, toothache, and colds. As soon as other pain medicines stop working, it starts working again.
- IT Band Stretch:
- Standing IT Band Stretch: Stand with your feet hip-width apart and cross the affected leg behind the other. Lean to the side, away from the affected leg, until you feel a stretch along the outer thigh and hip. Hold for 30 seconds, then switch sides.
- Hip Strengthening:
- Clamshell Exercise: Lie on your side with your hips and knees bent. Keep your feet together and lift the top knee towards the ceiling, then lower it back down. Repeat 10-15 times on each side.
- Hip Abduction Exercise: Lie on your side with your bottom leg bent for support. Lift the top leg towards the ceiling, keeping it straight, then lower it back down. Repeat 10-15 times on each side.
Prevention Strategies for Muscle Pain in the Knee:
While treatment methods can help alleviate existing muscle pain in the knee, adopting preventive measures is essential for reducing the risk of recurrence and maintaining overall knee health. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
- Warm-Up and Cool Down:
- Before engaging in physical activity, perform a thorough warm-up to prepare your muscles and joints for exercise.
- Incorporate dynamic stretches and light aerobic exercises to increase blood flow and flexibility.
- After your workout, cool down with static stretches to help prevent muscle stiffness and reduce the risk of injury.
- Use Proper Technique and Equipment:
- Whether you’re running, cycling, or participating in sports, ensure that you use proper technique and equipment to minimize stress on your knees.
- Wear appropriate footwear with adequate support and cushioning, especially if you





Leave Your Comment